| Bookmark Name | Actions |
|---|
Layers
This section explains layers of each microservice. It has three layers as shown in the below.
Business API Interface
It provides REST API interface for client application to interact with microservices.
- Business APIs are RESTful web service interface provided for external application to interact with Microservices.
- Open API Document is available for the client application and conforms to OpenAPI Specification 3.0.
- The supported media type is application or json.
- In the case of serverless deployment, API methods get configured as REST API endpoints in the respective API Gateway services to invoke the respective business functions
- In Docker deployment, CAMEL is used to host required REST services for business functions. Each business function gets registered as camel processor and REST URLs get configured using camel XML DSL.
Business Layer
It supports necessary business functions and uses entiry model for inquiry or persisting business data.
It has the data fields required for the API views. This model is used for passing data to the function and subsequently to the respective business logic layer. It is a Java bean, which represents input or output of business functions.
Data Type Validations
Microservice framework recognizes the enum datatype defied in the swagger spec. At runtime, the value passed in the payload will get validated against the possible values in the Enum data configured. If an invalid value is supplied at runtime, framework raises business exceptions.
These can listen for application events, that is, HTTP requests. Based on the event type, the implementation transforms the input data and invokes the required business functional implementation. These receive data in the form of View Model and invoke required business logic classes.
These can listen for event messages inbound into microservices.
In the case of the Ingester data event, it transforms event data into the data model and invokes required business logic classes.
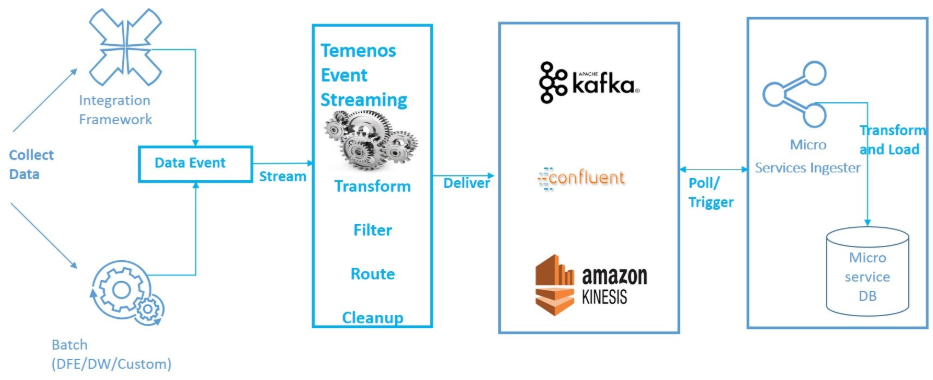
Ingester function is responsible to ingest near real time events into microservice database. Either ingester function polls the streaming platform for events (in Docker environment) or the streaming platform makes a function trigger whenever a new event is received (Cloud environment like AWS & AZURE).
Once the Ingester function receives the data, the data is serialized, transformed and persisted into the database in the required format.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
temn.tafj.runtime.use.df.cache=true |
TAFJ property specifies that Temenos Transact should start capturing events. Each Temenos Transact transaction emitting events produces exactly one record (data event) in the Temenos Transact events table (F.DATA.EVENTS) containing one or more sub events (Temenos Transact events) for each emitted event. |
|
RR.PARAM, I <application> |
RR PARAM specifies that the event capture is enabled for a specific application. |
Temenos Data Event Streaming (DES) is a highly scalable, elastic, distributed and fault-tolerant application to stream Temenos Transact events.
- It delivers on messaging or streaming solution (Kafka, AWS Kinesis)
- It delivers data in near real time
- At-least-once delivery guarantees (events are not lost)
- Schema-based event messages
The features of DES are:
- Event types
- Table update events;- Temenos Transact table (database) change
- IF business events - Temenos Transact business event from the Integration Framework
- Batch service events - Temenos Transact batch service emitting an event
- Event delivery
- Pull option - Fetches events by polling the events table
- Push option - Low-latency option to push event ids directly from Temenos Transact to the streaming platform
- At-least-once
- Event routing configurable through design-time
- Streaming platforms
- Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis
- Serialization
- Avro-binary messages
- Confluent Schema Registry
- Multi-part serialization of large events
From the DES platform, microservice ingester receives the below events:
- Table update events - It is a Temenos Transact table (database) change.
- IF business events - It is a Temenos Transact business event from the Integration Framework.
It is based on the format of JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), which is a lightweight and text-based data interchange format.
It stores a versioned history of all schemas and allows the evolution of schemas according to the configured compatibility settings. It also provides a plugin to clients that handles schema storage and retrieval for messages that are sent in Avro format.
Producer (DES) is responsible for the message serialization.
Consumer (Microservice framework Ingester) is responsible for the message de-serialization.
After the event message is generated in JSON array, it is transformed to the corresponding entity model by extracting the data from JSON array.
The transformed entity mode is persisted to database by microservice framrwork DAO factory layer in case of No Sql and by Spring JDBC template in case of Sql.
From the ingester, the data is updated in the sequence into the microservice DB. If there is any delay in the data, then the older data will not be stored into microservice DB.
Consider transaction1 and transaction2 are two transactions in Temenos Transact.
Before transaction1, insert it into MS DB. Transaction2 is processed and stored in MS DB. While processing the transaction1 in MS DB, it checks either the date is newer or older based on the filter. If the processing time of transaction1 is less than transaction2, then it will not be stored into the database.
@ExpiryFilter annotation is used to filter the older record value in DB by using this field.
For example, in PaymentOrder entity file, the processingTime field is used to store the payment date and time.
Using integration, test case sends two transaction data. The processing time for both the transactions differs in one second. The new data is stored in database.
The latest transaction record is stored in the database and the latest traction amount is 200.00.
The Business Layer classes are Plain Old Java Object (POJO) classes written in Java to implement the required business logic and validations. If required, it transforms data into a data model and uses Data Access Object (DAO) to query or persists data in the microservice data store.
Data Layer
It manages business data of the microservices and uses their persistence layer to persist data in SQL or NOSQL database.
Entity model classes are Java beans that represents data entities of respective microservices. These classes are used as a carrier to pass data on to or receive data from the data object layer.
Microservices Framework allows you to choose one of the below database:
- NoSQL database - The NoSQL DAO base classes hide the complexity and provide simple methods to support CRUD operations and selective patterns of Query methods. com.temenos.microservice.framework.core.data.NoSqlDbDao Interface provides query and persistence methods to be used to implement database operations in each of the microservices.
- SQL database - Spring JDBC Template framework is used to implement required database queries as part of the DAO layer.
Add Bookmark
save your best linksView Bookmarks
Visit your best links BACK
BACKIn this topic
Are you sure you want to log-off?