| Bookmark Name | Actions |
|---|
jBASE Remote File Service
This section provides insight on configuring jBASE Remote File Service (jRFS) driver on application servers to achieve remote access to files present on Database Server to form Multiple Application Server (MAS) architecture.
jRFS provides the following benefits:
-
It is possible to split application architecture from the database.
-
More than one application server can connect to a jBASE database.
-
For high availability, you can deploy Temenos Transact on two or more application servers.
-
Load sharing.
-
No single point of failure.
-
Provides access when there is a requirement to share the database between multiple systems.
Overview
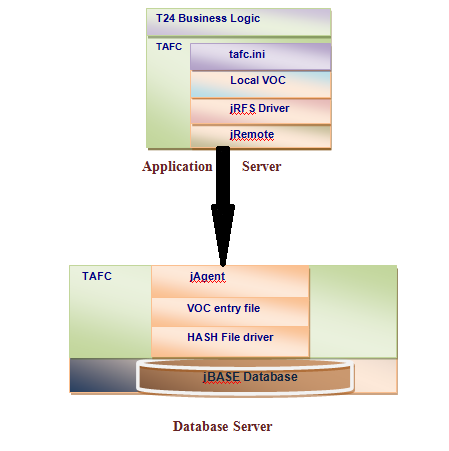
jRFS allows a Temenos Transact application to run on data kept on a separate server. This enables the architecture to split and thus helps in achieving load sharing on and high availability of an application server.
The jRFS driver requests in the form of either file access or query execution. These requests are sent from application server and are resolved at the database server. The resulting data is sent to the application server for further processing which can involve any Temenos Transact business logic.
Configuration of the jRFS driver is achieved through the tafc.ini configuration file, which defines where the database server’s jRFS Driver resides on the application server. The tafc.ini file is located under the $TAFC_HOME/config/$TAFC_CONTEXT directory.
At the database server, the "jAgent" daemon or service is started, which services requests sent from application server.
When a request is made from application server after the connection has been established with jAgent, the driver checks the stub file as pointed by the JEDIFILENAME_MD environment variable. This stub file contains file name of the VOC file present on the database server.
jFRS does not support access to UD file types from the application server access. In such cases, those directories on database server need to be NTFS mounted, so that they can be accessible from the Application server.
The use of the jstat command to retrieve the statistics of the remote file on the application server is not supported.
Installation
This section explains the database server and application server configuration.
jAgent is a service that resolves requests on the database server that are sent from application server. Therefore, jAgent should be running on the database server to process such requests.
Procedure
-
Before starting jAgent, set the JEDIFILENAME_MD environmental variable to point location of VOC file.
{export|set} JEDIFILENAME_MD = <location_in_which_VOC_file_is_present> -
Create a VOC entry for VOC under the VOC file itself. This entry is required by jRFS on application server. For example,
If the VOC file is present under /glodev2/Pareas/TestBase/TestBase.run/VOC, then create a record with name VOC as below specifying the absolute path:
AIX-/glodev2/Pareas/TestBase/TestBase.run: JED VOC VOC File VOC , Record 'VOC' Insert 16:22:16 Command-> 0001 F 0002 /glodev2/Pareas/TestBase/TestBase.run/VOC 0003 /glodev2/Pareas/TestBase/TestBase.run/VOC]D
-
Start jAgent on a specific port.
jbase_agent -p <port_number>
This section shows the environmental variables, configuration file and the Stub entry of the remote VOC filename required for application server configuration.
On the application server, set the following environmental variables:
| Environmental Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
JEDIFILENAME_MD |
Export or set this environmental variable to the location of the local stub file. |
|
TAFC_CONTEXT |
Export or set this environmental variable to default. In $TAFC_HOME/config directory, there are 3 directories present, namely default, multiapp and minimal. |
|
JDIAG |
Set this environment variable to turn on logging. JDIAG should be export or set to: jRFS=TRACE:filename=<name_of_the_log_file>
For example, export JDIAG=jRFS=TRACE:filename=first.log |
tafc.ini is the configuration file required by jRFS, which holds information related to remote database server to which application server should communicate.
Add an entry with [jrfs] as the section name under the tafc.ini file, located under $TAFC_HOME/config/$TAFC_CONTEXT.
Below is the format of [jrfs] section:
[jrfs] IPAddress=<IP Address on which jAgent is started> PortNumber=<Port number on which jAgent is listening> Username=<name of user> Password=<encrypted password> SSL={ON|OFF}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
IPAddress |
Database server IP address to which application server should communicate. |
|
PortNumber |
Port number on which jAgent is listening for the request. |
|
Username |
Name of the user. |
|
Password |
Password of the user. |
|
SSL |
Set to ON in case SSL encryption is desired else set to OFF. |
Example
As mentioned, there is another file which jRFS driver refers to on the application server.
Procedure
-
Create a normal file with contents as shown below:
JBC__SOB JediInitjRFS <Name of the remote VOC file present on the Database Server> -
Execute the following command:
export/set JEDIFILENAME_MD=<location of the local stub file>
Example
This section shows an example where a Windows machine is used as the application server and an AIX machine with IP address 10.92.5.15 is configured to work as database server.
You need to create a J4 file on the database server from the application server. For deployment, you need to:
-
Configure the database server (AIX).
-
Configure the application server (Windows).
-
Create J4 file on database server from application server.
-
Create VOC entry for the file created from the application server.
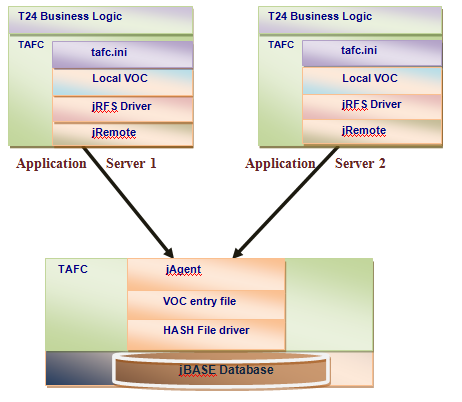
jRFS enables a split between the application server architecture and database. The application server only maintains a pointer to database VOC file. This makes it possible to have multiple application servers (MAS) pointing to the same instance of the database server.
The implication of this is that each application server has no direct, individual database storage, but shares access to a central database.
High availability is often associated with fault-tolerant systems. This means during any system fault, it is expected that the faulty component can either be quickly replaced or corrected with minimal interruption of service. Availability has long been a critical component for online systems because business processes can quickly come to a halt when a computer system is down.
This type of architecture assists in quick replacement of the application server, as it only requires configuring database server information on the application server and reference to database VOC file. It simplifies replacement of the application server during a failure or crash scenario (as data is always stored separately from the application server).
On database servers, Transaction Journaling facilities are available for recovery of any data lost due to a failure at database level.
Adding to our previous example, use a Linux machine as another application server connecting to the same database server.
In this example, create a record named FIRSTRECORD1 in the FIRSTFILE1 file, which was created in the previous example on the database server and will "LIST" its records from the new application server.
Procedure
-
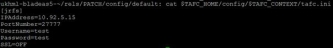
Update the tafc.ini file located under $TAFC_HOME\config\default with database server details. In this example, the tafc.ini file is updated as below:
-
Export TAFC_CONTEXT to the name of the folder in which tafc.ini is present. In this example, the tafc.ini file is located under the default directory of $TAFC_HOME/config.
export TAFC_CONTEXT=default
-
Create a normal file anywhere with any name. This will act as a stub file holding name of the remote VOC file. In this example, create a file name called localVOC under $TAFC_HOME. Below is the format of the content:
JBC__SOB JediInitjRFS <name of the database VOC file> -
Export the JEDIFILENAME_MD environmental variable to point the above VOC file.
export JEDIFILENAME_MD=$TAFC_HOME/localVOC
-
Set the JDIAG environmental variable to turn on logging on the application server:
export JDIAG=TRACE=jRFS
The above setting logs messages on the console.
export JDIAG=TRACE=jRFS:filename=newfile.log
The above setting creates newfile.log and logs all messages in this file.
The additional application server is now ready to communicate with the database server.
Add Bookmark
save your best linksView Bookmarks
Visit your best links BACK
BACKIn this topic
Are you sure you want to log-off?